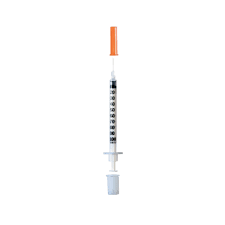
Insulin syringes are specialized devices used for the subcutaneous injection of insulin in individuals with diabetes. The 1ml insulin syringe is commonly used for administering U-100 insulin, which contains 100 units of insulin per milliliter.
Key Features
- Capacity: 1ml (100 units of U-100 insulin).
- Graduation: Marked in units to facilitate accurate dosing, typically graduated at every 1 or 2 units.
- Needle Gauge: Commonly available in gauges ranging from 30 to 31, with needle lengths typically between 6 mm to 8 mm.
- Design: Usually features a transparent barrel for easy reading of the dosage and a central nozzle for precise delivery.
Specifications
- Material: Made from medical-grade plastic (polypropylene and polyethylene) and stainless steel for the needle.
- Sterility: Packaged sterile for single use, conforming to ISO standards for safety and quality.
- Dead Space: Designed to minimize dead space to reduce waste, typically not exceeding 0.01 ml.
Indications
Insulin syringes are specifically designed for:
- Diabetes Management: Used by individuals with diabetes to self-administer insulin as part of their treatment regimen.
- Subcutaneous Injections: Suitable for delivering insulin into the fatty tissue just beneath the skin.
Usage Instructions
1. Preparation: Wash hands thoroughly before handling the syringe.
2. Filling the Syringe:
- Pull back the plunger to draw air into the syringe equal to the dose of insulin needed.
- Insert the needle into the insulin vial and push the plunger down to inject air into the vial, which helps in drawing out the insulin.
- Turn the vial upside down and draw the required amount of insulin into the syringe.
3. Administering the Injection:
- Choose an injection site (e.g., abdomen, thigh).
- Clean the area with an alcohol swab.
- Pinch the skin and insert the needle at a 90-degree angle (or 45 degrees if using a shorter needle).
- Push down on the plunger to inject the insulin, then withdraw the needle quickly.
Side Effects
While insulin syringes themselves do not cause side effects, improper use can lead to:
- Injection site reactions (redness, swelling).
- Hypoglycemia if too much insulin is administered.
Precautions
- Single Use Only: Insulin syringes should be disposed of after one use to prevent infections and ensure safety.
- Consult Healthcare Providers: Always consult a healthcare provider for proper dosing and injection techniques.